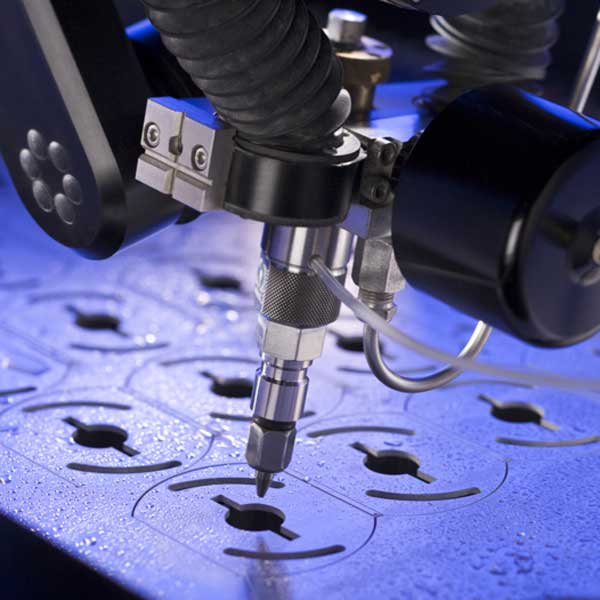
There are many advantages of choosing water jet cutting services. The technology allows the customer to cut through a variety of materials- thick, thin, large, or small- with pre-created designs or templates that are programmed into the CNC machining.
Water jets can cut materials ranging in thickness from .05” to 6.0”. Unlike laser and plasma cutting techniques, water jet cutting does not use heat, thus preventing morphing of hardened and heat-sensitive materials. While other styles of cutting can melt and change the structural components of materials such as plastics, water jet cutting is safe and allows the material being cut to keep its integrity.
Without manipulating the temperatures, water jet is also less wasteful and therefore more ‘green.’ There is no Heat Affected Zone (HAZ) to worry about, nor is there any smoke or dust produced. Water and abrasive mixtures are collected in a water-filled tank that catches the remaining residue, which can be recycled. With only small amounts of material lost due to cutting and recyclable run-off, water jet cutting is one of the more environmentally friendly material cutting options.
There are two methods of water jet cutting. One method, called pure jet cutting, simply uses tap water and the second method, abrasive jet cutting, mixes in an abrasive for more force. In either process, tap water is pumped through a filtration system towards several levels of pumps that gradually intensify the pressure. The water jet system is pressurized by hydraulically driven intensifier pumps, then moves to the shock attenuator that allows the outgoing water to maintain a steady output pressure. High pressure stainless steel tubing delivers the highly pressurized water to the cutting head nozzle. The head nozzle is made up of a jewel so that it is able to withstand the high pressure of the water without excessive erosion. The pressure of the water reaches rates as high as 60,000 pounds per square inch (psi), and as water travels through the jewel nozzle, the velocity of the water moves from Mach 2 to Mach 3 speeds. This is the process regardless of whether or not abrasive is used.
Garnet is one of the most commonly used abrasives in water jet cutting. Water and abrasive are mixed and focused in a beam to cut materials by supersonic erosion cleanly to close tolerances. If abrasive is utilized, it is mixed in a specially designed mixing chamber, then run through a precision disk that funnels like an hourglass to ensure a consistent, even flow. This chamber is located before the tap water meets the jewel head nozzle, which enables water jet cutting specialists to use virtually the same machinery for both pure jet and abrasive jet cutting processes. Abrasive is mixed in for cutting jobs that require more cutting force, while pure jet cutting is used for softer, more delicate materials such as paper goods. The abrasive mixture can easily be purged out of the initial water jet tubing after use, meaning the metering valve has the capability to turn the flow of abrasive on and off for multiple jobs. [/tab] [tab]Abrasive water jet cutting is essentially the same as the regular water jet cutting process, but with the addition of an abrasive gritty material to enable the water to cut through harder and thicker materials. Garnet is usually used as the added abrasive.
It still maintains the benefits of water jet cutting- no heat affected zone (HAZ), so there is no distortion of the material being cut, quick and easy programming, quick turnaround rate, accurate tolerances, less waste, potentially recyclable components used, CNC machine programmed, fast set up, no burrs, precision cutting. [/tab] [tab]Water jets and abrasive water jets can cut through a variety of materials, such as:
Brass
Copper
Steel
Titanium
Laminated
Shim Stock
Aluminum
Titanium
Nickel alloys
Hi-temp alloys
Cobalt
Inconel
Sheet goods
Alloys
Carbon Fiber
Composites
Leather
Stainless Steel
Wood
Plastics
Glass
Porcelain
Foam
Granite
Cork
Marble
Rubber
Natural Tile
Ceramic Tile
Engineered Tile
Natural Stone
Engineered Stone

